¶ EMBED Open Data FAQ
¶ What are the terms of use for EMBED Open Data?
The Data Use Agreement includes (but is not limited to) these important details you are agreeing to:
- The data must be used directly within an academic or other non-profit research organization under the direction of a lead principal investigator.
- You agree to only use the data for non-commercial, research purposes.
- You agree not to share, distribute, publish, or reproduce any portion of the data. If multiple people in your group would like access, please submit individual requests.
- You agree not to release/commercialize models (including foundation models), model-weights, or embedding spaces produced (in any way) using EMBED.
The full Data Use Agreement is available on our GitHub. Please familiarize yourself with it before using EMBED Open Data.
¶ How can I get access to EMBED Open Data?
EMBED Open Data is available for non-commercial research use for members of academic and other non-profit research institutes. If you'd like to request access to the dataset, please submit an application to our online form.
Please ensure your proposed project meets the terms of the Data Use Agreement before submitting your application.
¶ Will I be charged for downloading the dataset from AWS?
No, as part of the AWS Open Data Program, egress costs have been waived for EMBED Open Data. Please note you will still incur ingress costs if you download the dataset into an AWS resource that you own (such as a personal/lab S3 bucket) instead of a local directory.
¶ How large is EMBED Open Data?
EMBED Open Data contains 480,323 images (76% 2D and 24% synthetic-2D) collected during 76,373 breast imaging exams from 22,382 patients at Emory healthcare centers between 2013 and 2020. The total dataset is approximately 2.5TB and consists of a clinical data table, an image metadata table, and the images.
If space is a concern, we recommend downloading just the files in
s3://embed-dataset-open/tables/first (the tables are <1GB), then using them to identify the subset of images in your cohort. Individual images can then be downloaded with their file paths using a bash script or a python script with the boto3 package.
¶ Which image modalities are included in the Open Data version?
At the moment, the Open Data version of EMBED contains the 2D and synthetic-2D ('c-view') images for the included patients. We're planning to add the DBT, US, and MRI images for these patients in the future when version 2 of EMBED is completed.
¶ What does this clinical variable mean?
The best resource for meanings/values of clinical variables in EMBED Open Data is the data dictionary in the GitHub repository. The documentation on this website also describes some of the most commonly-used features on the Overview and Label Assignment pages.
¶ How do I generate my AWS Access Key/Secret Access Key?
Once your AWS ID has been added to the Open Data S3 bucket configuration, you'll need to configure your AWS client of choice (AWS CLI / rclone / boto3 / other) using your personal Access Key and Secret Access Key. If you haven't generated one yet, you can follow the steps below to generate them for your root AWS Account.AWS provides granular access control methods. If you use your account for other tasks, we recommend consulting their documentation for access management with IAM roles. By default we set up access for the root of the account, so please contact us if you need us to specify a role in our access policy (please include the role ARN in your email).
¶ Step 1: Go to the 'Security Credentials' page
First, log into the AWS Console and open the account settings dropdown menu by clicking on the tab in the top right corner of your screen. Click on the 'Security Credentials' link on the dropdown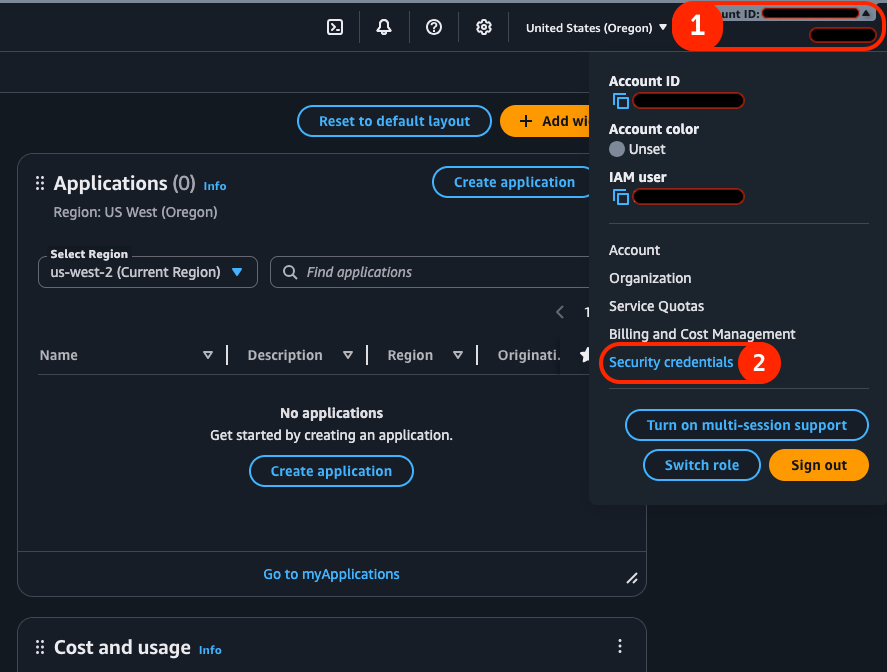
¶ Step 2: Create a new access key
After opening the 'Security Credentials' page, scroll down until you see a section titled 'Access Keys'. Click on the 'Create Access Key' button on the right side of this section.
¶ Step 3: Review usage options
You should now see a screen listing access use-cases and recommended options. If you'd like to proceed with a root access key select 'Command Line Interface (CLI)' or 'Other', then 'Next' to continue. Otherwise, review the AWS documentation to set up a fine-grained access control method.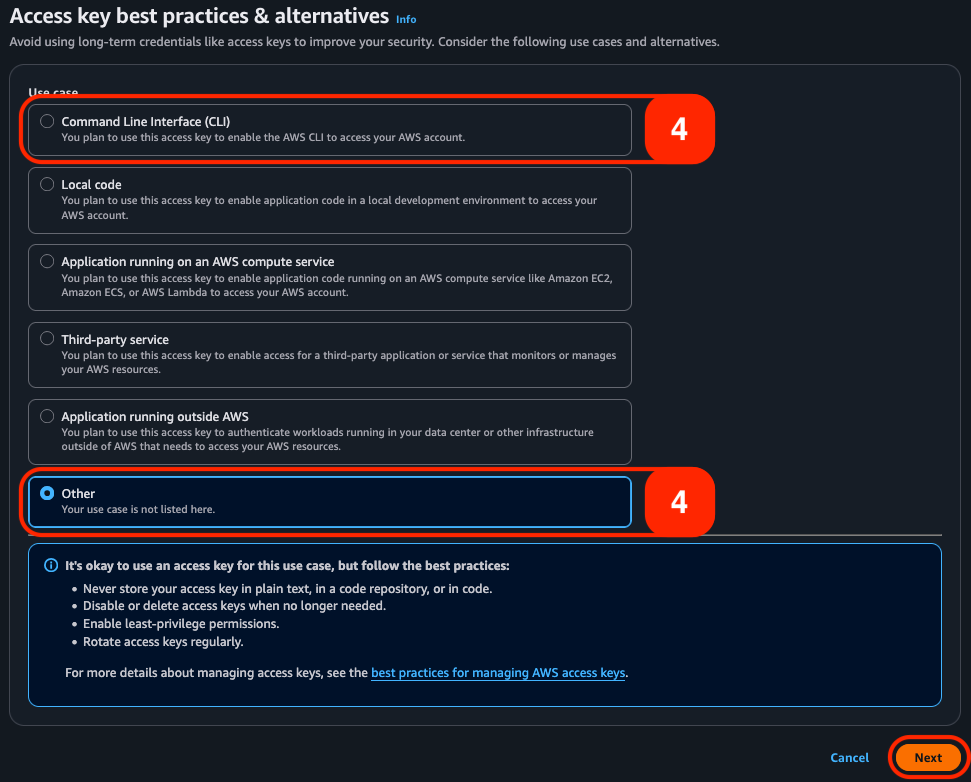
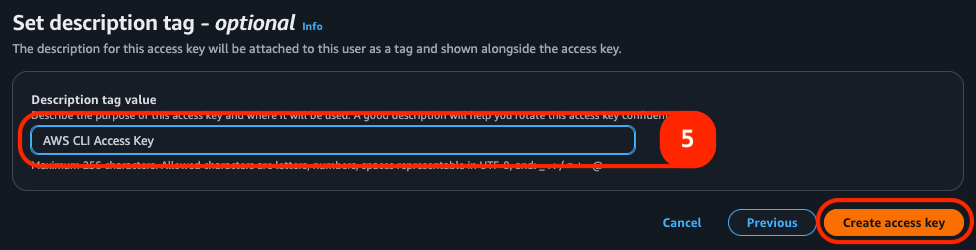
¶ Step 4: Finalize your access key
Finally, you can choose to name your Access Key (if you'd like to do so) then create it with the 'Create Access Key' button in the bottom right corner. Your Access Key and Secret Access Key will be shown on the following page.Your Secret Access Key will only be visible this single time, so please ensure that you record it somewhere secure. If you lose your Secret Access Key you can generate a new one using these steps.
Your Access Key/Secret Access Keys should never be shared with anyone or stored as plaintext.